4G VS 5G
1, first and foremost, LTE-based 4G networks are undergoing a rapid deployment, while 5G networks are currently only in the research and implementation project phase, with large-scale deployments expected to take place until 2020.
2, 4G and previous mobile networks focused primarily on the provision of raw bandwidth, while 5G was designed to provide ubiquitous connectivity and lay the foundation for fast, elastic network ingresss, whether users are in skyscrapers or subway stations.
3, 5G network will not exist independently, it will be a combination of technologies, including 2G, 3G, LTE, LTE-A, Wi-Fi, M2M and so on. In other words, 5G is designed to support many different applications, such as the Internet of Things, connected wearables, augmented reality, and immersive gaming.
4, unlike 4G, 5G network has the ability to handle a large number of networked devices and traffic types. For example, 5G provides ultra-high speed links when working on high-definition video online playback tasks. When faced with a sensor network, it only provides a low data transfer rate.
5, 5G networks will be the first to use new architectures such as cloud RAN and virtual RAN to promote a more centralized network and maximize the use of server farms through localized data centers at the edge of the network.
6. Finally, 5G will also take the lead in using perceptive radio technology to enable the network infrastructure to automatically determine the type of band that is available, to distinguish between mobile and fixed devices, and to adapt the current situation within a certain time frame. In other words, 5G networks can serve both industrial networks and Facebook apps.

 Networking
Networking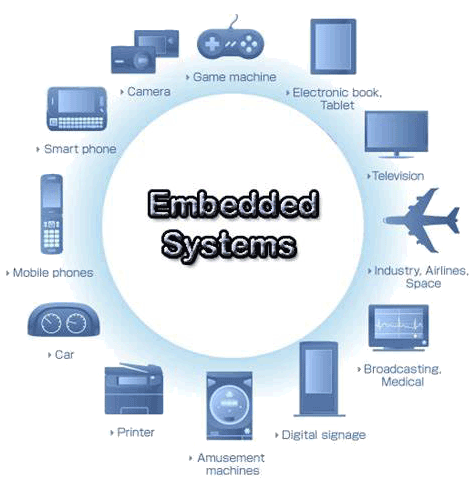 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Switches
Switches Wireless Solutions
Wireless Solutions Industrial Computer
Industrial Computer Cloud Services
Cloud Services



