Classification of E-lins 4G industrial routers
There are many types of 4G industrial routers, which can be divided into different categories from different perspectives. Different types of 4G industrial routers can be used in different environments. The following sections classify the 4G industrial routers from different perspectives.
According to the performance
From the perspective of performance, 4G industrial routers can be divided into linear router and non-linear router.
The so-called wire speed router can transmit freely according to the transmission medium bandwidth, basically without discontinuity and delay. The specific calculation method is the same as that of the switch line speed backplane bandwidth. A wire-speed router is a high-end router with very high port bandwidth and data forwarding capability that forwards packets at the media rate.
Non-wire-speed routers are mid – to low-end routers, but some new wire-access routers also have wire-speed capabilities. The performance of router is mainly affected by CPU performance. If the CPU performance is high, the 4G industrial router is more likely to be a high-performing wire-speed router.
Speed is generally not a measure of a router, and data throughput is one of the references used to measure a router’s maximum data throughput. The routers with the capacity of the rear plates of 4G industrial routers greater than 40Gbps are called high-grade routers. The routers with the capacity of the rear plates between 25Gbps and 40Gbps are called midrange routers, while those with the capacity lower than 25Gbps are considered as low-grade routers. This kind of dividing way is not so absolute, specific parameter needs to make distinguishing according to each manufacturer specific parameter.
According to the structure of the points
The 4G industrial routers can be divided into modular router and non-modular router according to the structure Angle.
Modular routing generally only provides basic routing function when leaving the factory. Its interface type and partial extension function are configured according to the actual needs of users. Users can choose corresponding modules according to the network type they need to connect. Different modules can also provide different connectivity and management capabilities. For example, the vast majority of modular routers allow users to choose network interfaces, VPNS, firewalls and other functions, most of which are modular routers.
Non-modular routers are mostly low-end routers, which are mostly used in civilian environments. Primarily used to connect small business customers within homes or isps, supporting virtual private network protocols such as SLIP, PPP, PPTP, and IPSec. These protocols to run on each port, such as ADSL will increase home broadband availability, which will increase the burden of accessing routers. In the future, such router ports will run multiple protocols while avoiding the telephone switched network.

 Networking
Networking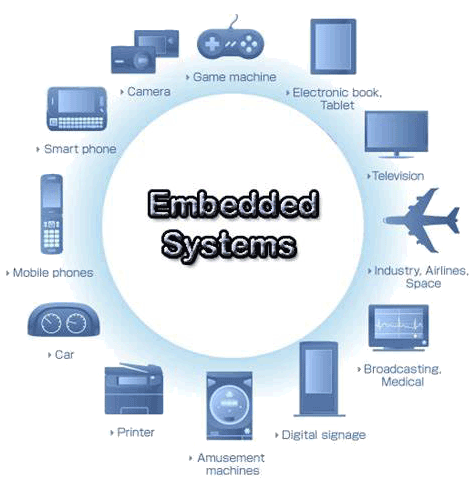 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Switches
Switches Wireless Solutions
Wireless Solutions Industrial Computer
Industrial Computer Cloud Services
Cloud Services



