Exchange mode of the switch
Switching is a general term for technologies that send the information to be transmitted to the corresponding route that meets the requirements by manual or automatic equipment according to the needs of transmitting information at both ends of the communication. According to different working positions, it can be divided into wide area network switch and local area network switch. Wide-area switch is a kind of equipment that completes the information exchange function in the communication system.
Three exchange methods of the switch:
1) Straight-through type:
The straight-through Ethernet switch can be understood as a line matrix telephone switch that crosses vertically and horizontally between each port. When it detects a data packet at the input port, it checks the header of the packet, obtains the destination address of the packet, activates the internal dynamic lookup table to convert it into the corresponding output port, connects at the intersection of input and output, and passes the data packet directly to The corresponding port realizes the switching function. Since no storage is required, the delay is very small and the exchange is very fast, which is its advantage. Its disadvantage is that because the content of the data packet is not saved by the Ethernet switch, it cannot check whether the transmitted data packet is wrong, and it cannot provide error detection capabilities. Because there is no buffer, input/output ports with different speeds cannot be directly connected, and packets are easily lost.
2) Store and forward:
The store-and-forward method is the most widely used method in the field of computer networks. It stores the data packet of the input port first, and then performs CRC (cyclic redundancy check) check. After processing the error packet, it takes out the destination address of the data packet, and converts it into the output port through a lookup table to send out the packet. Because of this, the store-and-forward method has a large delay in data processing, which is its shortcoming, but it can perform error detection on the data packets entering the switch and effectively improve the network performance. It is especially important that it can support the conversion between ports of different speeds and maintain the cooperation between high-speed ports and low-speed ports.
3) Fragment isolation:
This is a solution between the first two. It checks whether the length of the data packet is enough for 64 bytes, if it is less than 64 bytes, it means it is a fake packet, then discard the packet; if it is greater than 64 bytes, then send the packet. This method also does not provide data verification. Its data processing speed is faster than store-and-forward, but slower than straight-through.

 Networking
Networking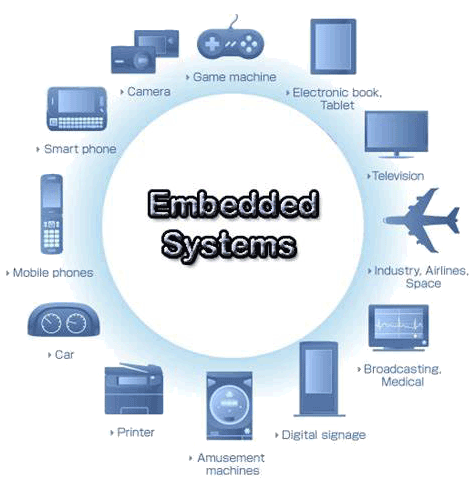 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Switches
Switches Wireless Solutions
Wireless Solutions Industrial Computer
Industrial Computer Cloud Services
Cloud Services



