Industrial 4g sim router’s function and the way it works
A router is the first line of security from intrusion into a network. Enabling the highest level of security on the router turns on things like the firewall, and is the best way to keep your computer system and information safe from attack.
Most Industrial 4g simrouters connect to other network devices only with network cables and don't require drivers to operate in Windows or other operating systems. However, routers that connect to a computer with a USB or FireWire typically require drivers to operate correctly.
Routers often act as the DHCP servers in small networks, issuing unique IP addresses.
Routers connect a modem—like a fiber, cable, or DSL modem—to other devices to allow communication between those devices and the internet. Most routers, including wireless routers, usually feature several network ports to connect numerous devices to the internet simultaneously.
The IP address assigned to the WAN or internet connection is a public IP address. The IP address assigned to the local network connection is a private IP address. The private IP address assigned to a router is usually the default gateway for the various devices on the network.
Wireless routers, and wired routers with multiple connections, also act as simple network switches allowing the devices to communicate with each other. For example, several computers connected to a router can be configured to share files and printers among each other.
Routers are like small computers, with a CPU and memory to deal with incoming and outgoing data. Different software, such as DD-WRT, can be loaded on the router, much like an operating system on a computer.
A router operates on the Network layer (layer 3) of the OSI model and uses routing tables to understand where traffic is coming from and where it should go.

 Networking
Networking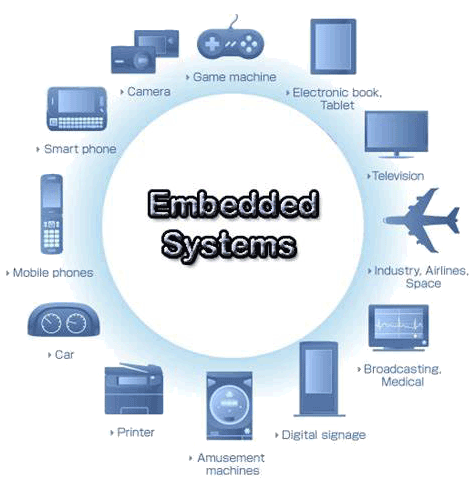 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Switches
Switches Wireless Solutions
Wireless Solutions Industrial Computer
Industrial Computer Cloud Services
Cloud Services



