LTE CAT1 to CAT10, and CAT0
Cat. Is UE-Category. According to the definition of 3GPP, UE-Category is divided into 10 levels from 1 to 10, where Cat.1-5 is defined by R8, Cat.6-8 is defined by R10, and Cat.9-10 is R11 definition.
LTE CAT, the popular explanation is the level of 4GLTE network transmission rate that user equipment can support, which can also be said to be a technical standard for 4G network speed. Therefore, LTE CAT4 / CAT6 means that the user equipment's LTE network access capability level is 4 or 6.
Since the levels are different, their capabilities are certainly not the same. Let's take a look at what performance is affected by LTE CAT4 / CAT6, and at what level. To put it simply, LTE CAT affects the upper limit of 4GLTE uplink and downlink network speeds. Generally speaking, the maximum upload and download speeds that user equipment can achieve.There are not only two levels of 4, 6 in LTE CAT.
UE Category
Max date
download rate
(Mbps)
Max date upload
rate
(Mbps)
Max.#.spatial
layers
Category1
10
5
1
Category2
50
25
2
Category3
100
50
2
Category4
150
50
2
Category5
300
75
4
Category6
300
50
2or4
Category7
300
150
2or4
Category8
1200
600
8
The above table lists the known LTE CAT levels and their corresponding maximum transmission speeds. Among them, LTE CAT4 / CAT6 is also the network transmission technology level of 4G mobile phones, and the faster CAT10 has been commercially developed.
Why define Cat.0?
To cope with the Internet of Things, LTE-M (M2M) must optimize the LTE network in several ways:
1) Equipment cost: In order to reduce equipment cost, R12 has established Cat.0 terminal level. In fact, Cat.0 refers to low-cost M2M equipment. When the equipment transitions from the connected state to the idle state, the timer starts running. . When the timer expires, the device enters power saving mode. When the device enters the power saving mode, the device no longer receives paging messages. It seems that the device and the network are disconnected, but the device is still registered in the network. The device will remain in this power saving mode until the device needs to actively send information to the network.
2) Battery life: When the device transitions from the connected state to the idle state, the timer starts running. When the timer expires, the device enters power saving mode. When the device enters the power saving mode, the device no longer receives paging messages. It seems that the device and the network are disconnected, but the device is still registered in the network. The device will remain in this power saving mode until the device needs to actively send information to the network
3) Enhanced coverage: For IoT M2M applications, coverage is also very important. As a simple example, smart water meters are installed in basements or hidden places inside buildings. Due to signal attenuation, the signal is usually weak in these places. Therefore, it is necessary to improve and enhance network coverage to cope with the Internet of Things.

 Networking
Networking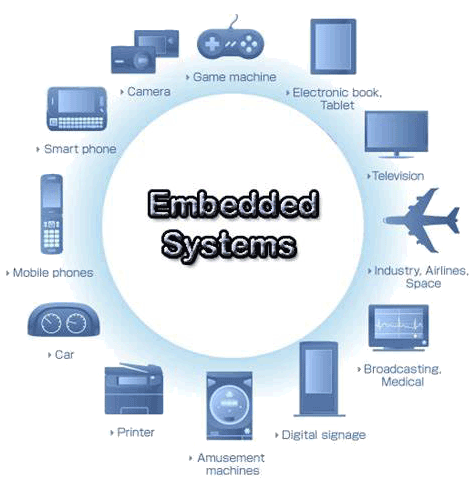 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Switches
Switches Wireless Solutions
Wireless Solutions Industrial Computer
Industrial Computer Cloud Services
Cloud Services



