The best 4g router with load balancing
A web architecture without load balancing looks like this: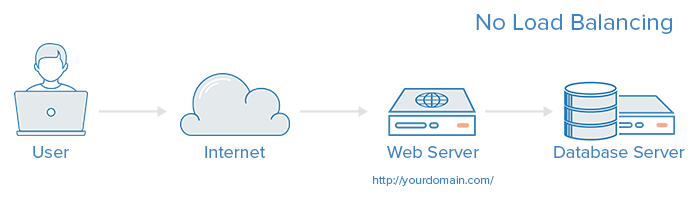
Here the user is directly connected to the web server. If the server is offline, the user will naturally not be able to access it. In addition, if many users try to access the server at the same time and exceed the limit of its processing capacity, the loading speed will be slow or the connection will not be possible at all.
This failure can be alleviated by introducing a router with load balancing function or at least one additional server in the backend. Under normal circumstances, all back-end servers will guarantee to provide the same content so that users can receive the same content no matter which server corresponds.
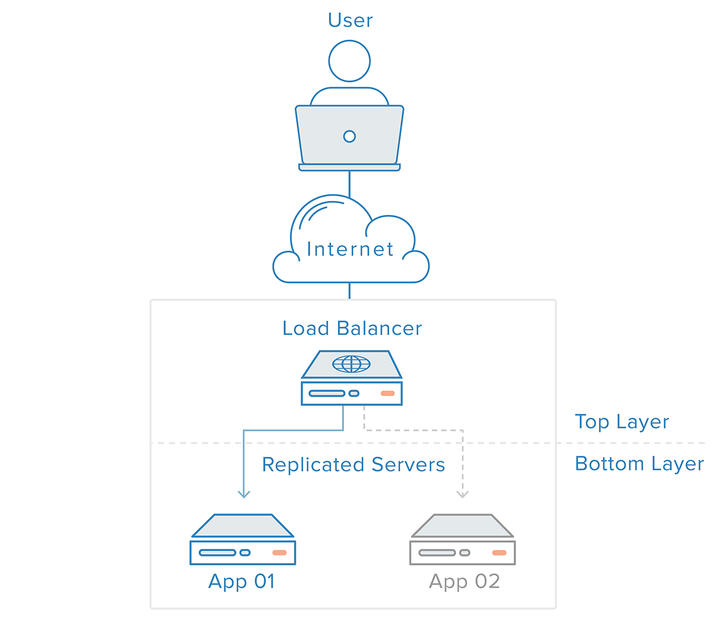
As you can see from the figure, the user accesses the load balancer, and the load balancer forwards the request to the back-end server. In this case, the single point of failure has now been transferred to the load balancer.
The best 4g router with load balancing, H685 can use embedded 4G module, RJ45 WAN and WiFi client connection at the same time, and share these WAN connections with LAN users. Through channel link bonding, the H685 4G router can combine two or more links to achieve redundancy or increase throughput. The difference between channel binding and load balancing is that load balancing divides the traffic between network interfaces on the basis of each network socket (layer 4 of the OSI model), while channel binding is for each data at a lower level The physical interface of the packet (OSI model) is divided between the traffic layer 3) or the data link (OSI model layer 2) basis.

 Networking
Networking EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Switches
Switches Wireless Solutions
Wireless Solutions Industrial Computer
Industrial Computer Cloud Services
Cloud Services



