the best industrial 4G sim slot routers improved?
In what ways has the network control capability of best industrial 4G sim slot routers improved?
Traditional industrial 4G sim slot routers cannot guarantee performance and control functions at the same time. Control functions are provided by a series of rules, such as priority, denial of access, or provision of accounting data. When a data packet enters an industrial 4G router, these related rules also apply to the data packet. In software-based routers, these rules are stored in a software database, and each data packet must be checked against the database when it passes. This is the source of the problem: the microprocessor that handles the routing function must also query the database. At this time, the data packet will not be sent, so the forwarding capability of the dual-card router is low.
The new generation of switched industrial GPRS routers will not encounter this problem, because the query and control functions are implemented in hardware. The key to the combination of switching router performance and control functions is how much the ASIC can read the content of each data packet.
The more information about the flow of each data packet that ASIC can collect, the finer the level of control that can be applied to that data packet flow. Each client/server conversation generates a series of data packets between the client and the server. The data stream composed of these data packets of the industrial GPRS router can be identified in the second, third or fourth layer of OSI respectively. Each layer will provide more detailed information about the flow. The most basic job of managing a network is to control these network traffic. At layer 2, each data packet in the data stream is identified by the MAC address of the source site and destination site. At layer 3, industrial CDMA router data streams are identified by source and destination network addresses, and the ability to control data streams is limited to source/destination address pairs, such as the switched industrial-grade CDMA called Layer 3 switches on the market now router. If a client is using multiple applications on the same server at the same time, the layer 3 information will not describe each application flow in detail, so that it is impossible to implement different control rules for each data flow. .
Traditional routers across the entire network have the ability to read the layer 4 header information. In fact, most of the advanced control features in traditional industrial full Netcom routers are implemented on layer 4. For example, in a software-based industrial-grade full Netcom router, layer 4 information is used to establish a security filter, which is an important part of the process of controlling network traffic. But for software-based full Netcom routers, for the reasons mentioned above, in-depth reading of data packets will greatly sacrifice performance. Indeed, in many software-based industrial routers, performance can drop by up to 70% when security filters are enabled.

 Networking
Networking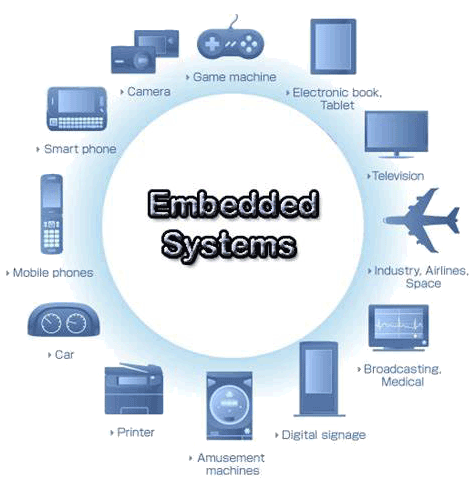 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Switches
Switches Wireless Solutions
Wireless Solutions Industrial Computer
Industrial Computer Cloud Services
Cloud Services



