The main protocols and functions of 5G industrial routers
The main protocols and functions of 5G industrial routers:
1. Reliable networking and communication: select high-performance industrial-grade 5G wireless modules, industrial-grade high-stability and high-precision components, -35~+75C extremely wide temperature planning, easy to get used to high temperature and cold working environment, and provide a reliable supply for unattended systems Networking and secure communication.
2. Improved data processing and transmission speed: CPU processing speed increased by 3 times, WIFI transmission speed increased from 54Mbps to 150Mbps, built-in FLASH, RAM capacity increased by 2 times, satisfying the needs of large data volume wireless transmission, such as images, videos, etc., more clear and clear .
3. Supporting supply equipment processing channels: support the gathering processing, batch configuration and upgrading functions of many equipment, making the implementation and processing of large projects more efficient.
4. Bandwidth capital allocation is controllable: new traffic control, traffic recording, real-time network speed display function, it can be handled in accordance with the type of network protocol and pre-customized bandwidth allocation form.
5. Strong WIFI: WIFI supports 802.11b/g/n, supports WIFIAP, APClient, repeater, relay bridge and WDS, etc., and supports WEP, WPA and other encryption methods, satisfying more WIFI communication needs. WIFI adopts built-in integrated planning, which can effectively improve the stability of the product.
6. High-speed processing CPU: Using an industrial-grade CPU with a higher speed than the original ARM9, it can process various protocol data conversions at a higher speed, avoiding data retransmission and loss caused by slow CPU processing speed.
IGRP is a proprietary protocol for industrial entire network routers and is only implemented in industrial 5G routers. It also belongs to the distance vector protocol, so it has something in common with dual router RIP in many places, such as broadcast update and so on. The biggest difference between RIP and RIP lies in several aspects such as measurement methods and load balancing. IGRP supports weighted load balancing on multiple paths, so that the network bandwidth can be used more reasonably. In addition, unlike RIP, which only uses the number of hops as the metric, the dual-card router IGRP uses a variety of parameters to form a composite metric. The factors that can include: bandwidth, delay, load, reliability, and MTU (maximum transmission Unit) and so on.

 Networking
Networking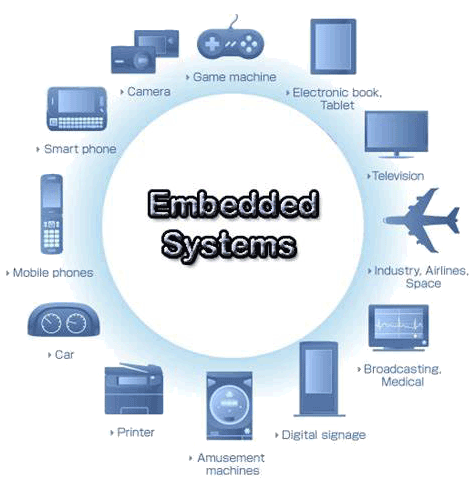 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS Switches
Switches Wireless Solutions
Wireless Solutions Industrial Computer
Industrial Computer Cloud Services
Cloud Services



